

Multifunction Devices (MFDs) perform multiple office imaging tasks, such as input, output, storage, and transmission of documents. They feature Canon's cutting-edge technologies, such as its advanced network, document processing, and software technologies.
2018/12/27Featured Technology
#Technology in Products#Printer
Laser printers / laser multifunction printers (MFPs), office multifunction devices (MFDs), and digital production printing systems all employ the same printing principle.
1 Charging
The photosensitive drum surface is negatively charged with a static charge.
2 Exposure
Laser beams scan the photosensitive drum to form an image. Areas exposed to the laser beams lose their electrical charge.

3 Developing
Toner is brought in close proximity to the drum and affixes to non-charged areas.

4 Transfer
The photosensitive drum is brought into contact with the paper* and a positive charge is applied from behind, transferring the toner onto the paper.

5 Fixing
Heat and pressure are applied to fix the toner to the paper.
#IoT#Computer science
Canon's imageRUNNER ADVANCE Office MFDs are a new type of MFD developed ahead of the competition based on a user-centric concept. They were designed not only for ease of use as Office MFDs, but also for networking with office PCs or other imageRUNNER ADVANCE Office MFDs for increased operation efficiency.
One of the core functions supporting this system networking is the Advanced Box / Advanced space function, which makes use of the built-in HDD (hard disk drive) to offer both MFD box functions and simple file server functions. This was achieved by creating a new document management module within the OS file system layer. The new document management module incorporates embedded application modules for controlling the operation of each of the Advanced Box / Advanced space, network (SMB, WebDAV), and memory media repositories,*1 allowing users to use the Advanced Box / Advanced space without having to worry about discrepancies between repositories.
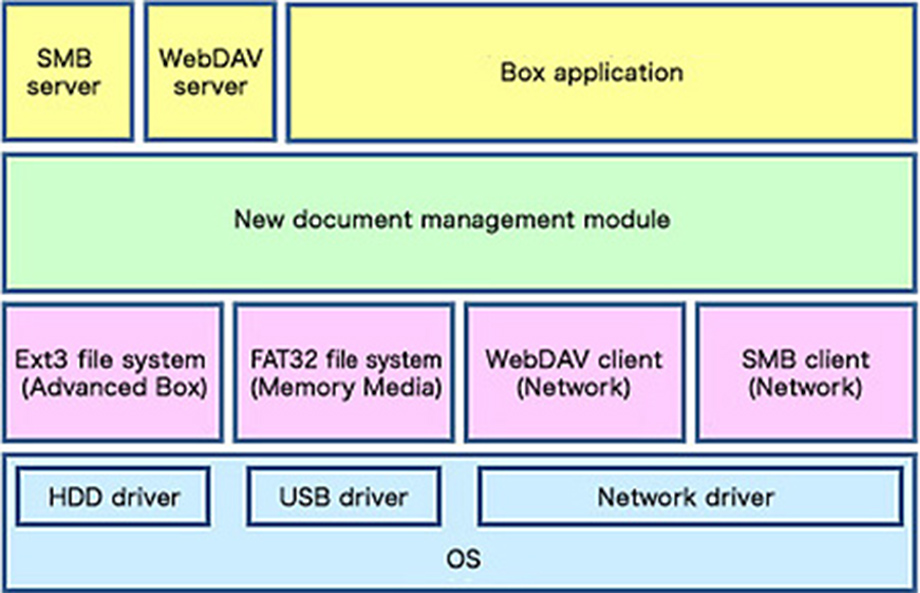
Advanced Box / Advanced space -Related Software Structure
The Advanced Box / Advanced space function offers compatibility with multiple standard protocols, such as SMB and WebDAV, for enhanced adaptability with various network environments in the emerging era of cloud computing. Providing the Office MFDs with both server and client functionality for the two protocols makes it possible to link imageRUNNER ADVANCE machines together in a network, as well as with PCs.
The Advanced Box / Advanced space functionality enables access to data on Office MFDs in the same way as accessing a file server, with no need to install special applications on a PC. For example, a printed PowerPoint presentation can be scanned and saved in the Advanced Box / Advanced space in both PowerPoint and PDF file formats, enabling access and use at any time from a PC without having to prepare a separate file server.
Even imageRUNNER ADVANCE machines not equipped with HDDs can connect to other imageRUNNER ADVANCE systems connected via intranets, to be used as if they had their own Advanced Boxes / Advanced spaces.
Additionally, the address book sharing function allows any imageRUNNER ADVANCE system to look up and use registered address information simply by registering addresses used by multiple parties within an office on a single imageRUNNER ADVANCE machine connected via an intranet. The address book framework was built based on the WebService platform offered by Canon's Office MFDs, ensuring its scalability*2 and making possible the sharing of address books across multiple Office MFDs on the same network. Enhanced connectivity between multiple imageRUNNER ADVANCE MFDs, and between the MFDs and PCs, supported by address book sharing and other functions, has led to significant advances in office workflow.
#Social contribution#Computer science
In offices, MFDs serve as hubs for the input and output of documents. As companies become more dependent on networks and documents grow increasingly important, there is a greater need for advanced security similar to that of PCs. Canon MFDs employ a number of network and information security functions, and the company continually strives to further improve these features so that customers can use their MFDs with peace of mind.
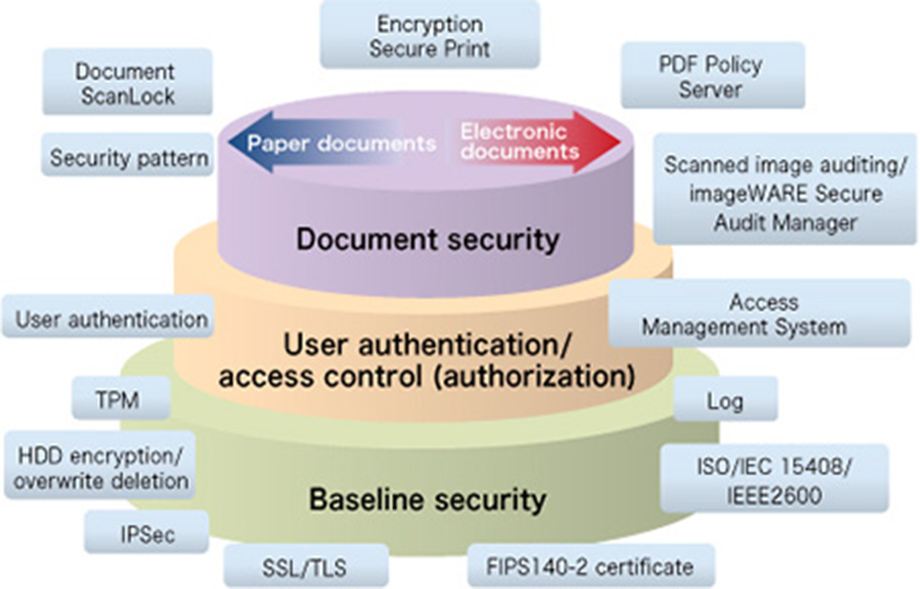
Overview of Canon Office MFD Information Security Technology
Office MFDs, like workstations and servers, store a great deal of confidential information within their internal memories, including passwords and encryption keys. The TPM (Trusted Platform Module)*3 plays an important role in protecting the confidential information contained in MFDs from physical analysis and unauthorized network access. All confidential information is encrypted using the root key on the TPM chip before being stored. The root key never leaves the chip, ensuring the protection of confidential information within the Office MFD.
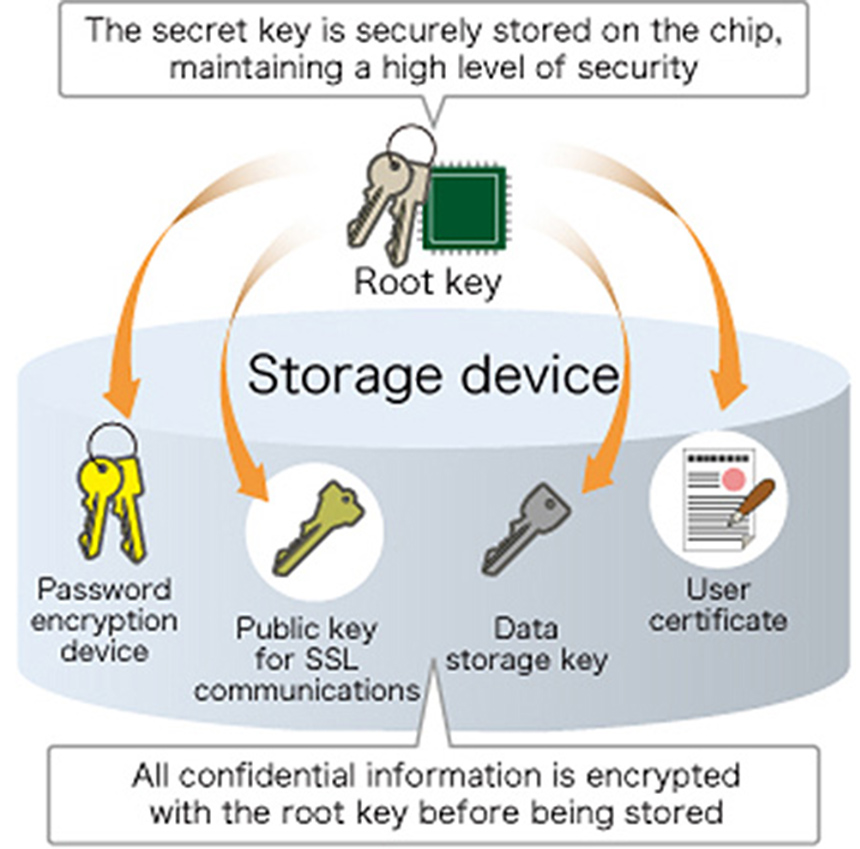
Key Management Module
Access Management System technology prevents unauthorized device usage by restricting which functions can be used on a per-user basis. IT administrators can set in advance which functions can be used by which users so that users will only see the screens for which they have been granted usage permission.
ACTs (Access Control Tokens)*4 are used when sending print orders from PCs to Office MFDs, making it possible to implement print restrictions and prevent print data tampering and replaying.
Canon's MEAP application platform optimizes Office MFDs for office operations. MEAP can easily be customized to work with existing company security systems, such as employee management systems, Smart card authentication and Active Directory.*5
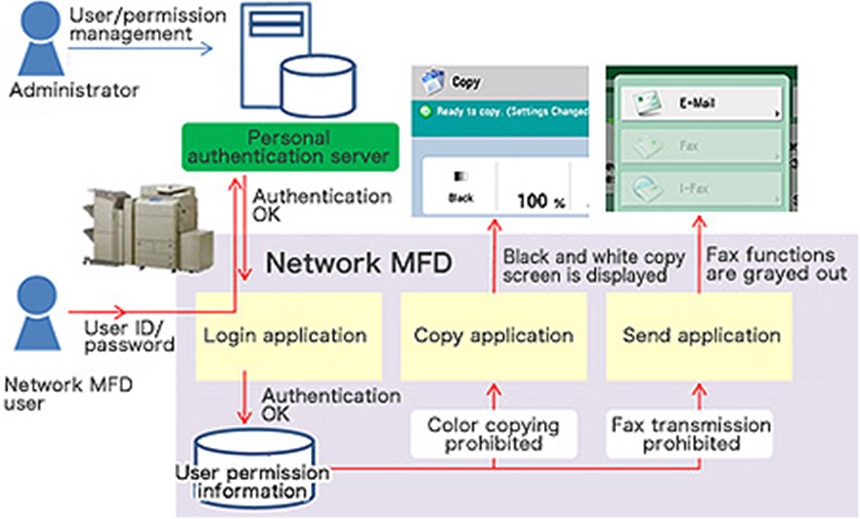
Access Management System Structure
Studies have shown that 74.9% of information leaks originate from paper documents.*6 To prevent the unauthorized copying of paper documents containing confidential information, Canon has developed TL Code (Trace & Lock Code), a 2-D code technology. Office MFDs print TL code onto the background of a document when printing. Should an unauthorized user attempt to copy that document, the Office MFD will rapidly analyze the information contained in the TL code and respond in such ways as preventing the confidential document from being copied or identifying the user that printed the document.
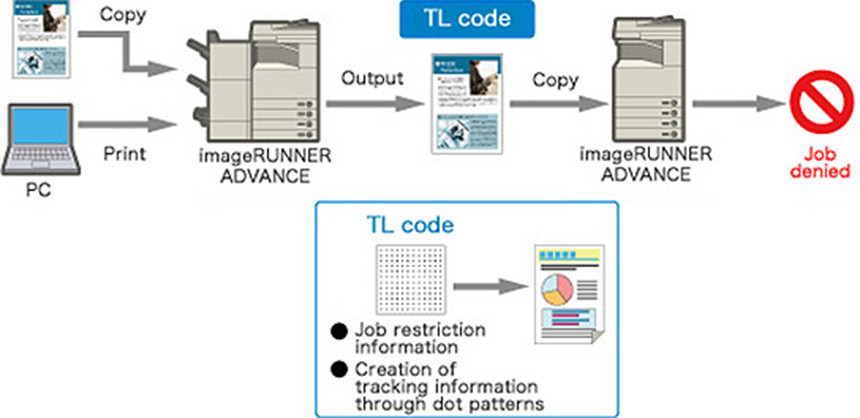
Overview of TL Code-Based Job Restrictions
In June 2009, the IEEE Std 2600.1™-2009 and IEEE Std 2600.2™-2009 international standards (hereafter, IEEE 2600) were established to govern MFD and printer security technologies. Canon was one of the companies that participated in the creation of these standards. In March 2011, after passing rigorous evaluations, including site visits to inspect manufacturing processes at overseas production sites, Canon successfully obtained Common Criteria certification conforming to IEEE 2600 from IPA (Information-Technology Promotion Agency, Japan).
#IoT#Computer science
In recent years, there has been an increase in services involving the cloud-based handling of in-house and external file management, business systems including labor, HR, accounting, and sales, and industry-specific support software for such fields as education, medicine, finance and law. In response, Canon has developed its own cloud platform for offices. By connecting MFDs to cloud services, Canon is increasing the productivity of office operations.
This platform possesses two main functions:
These functions incorporate many technologies, including data processing technology to simplify cloud service processing, connection/communication technology for sending/receiving data between MFDs and the cloud, encryption technology that protects data on communication channels, multi-tenant architecture that prevents data leakage in situations where multiple companies jointly utilize one cloud environment, and authentication technology that limits MFD users.
#Electrical engineering#Computer science
Office MFDs that carry out concurrent processing such as printing and scanning handle enormous volumes of data. Because of this, the heart of such products needs to efficiently process multiple functions. Canon is developing dedicated processors to suit these products.
To increase overall system performance and the ability to respond to solutions, the "Advanced iR Controller" is made up of an image processing controller section equipped with an image processor, and an information processing controller section equipped with an information processor. Not only is processing speed maximized by connecting these two controllers using a high-speed PCI Express bus, but it is also possible to adapt to the evolution of document workflows by optimizing each of the controller sections.
The imaging processor incorporates advanced image processing technologies in addition to providing faster printing and scanning, which are the basic functions of an Office MFD. The information processor boasts excellent compatibility with the network and Internet environments and provides many new functions by coordinating security functions and connections with external systems.
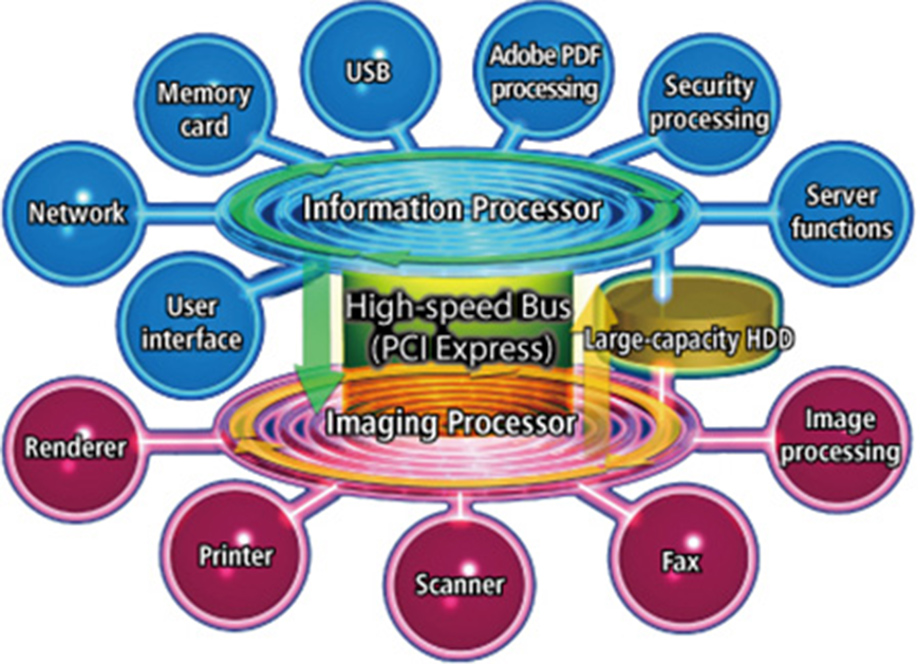
Overview of the Advanced iR Controller
Printing A4 sized image data at 600dpi in full color requires 100MB of image storage space. To process this quickly, compression technology must be fast and highly efficient.
VL (Visually Lossless) compression technology is one of the many image processing technologies used in the imaging processor. This unique Canon image compression technology appropriately balances the image quality and compression ratio of PDL*7 data.
When a command is received from a PC to print PDL data, the system first divides the data up into many small tiles. The segmented image data is sent, in random order, to the compression engine, where it is processed. What makes this technology notable is that when this happens, it automatically divides the data into two types.
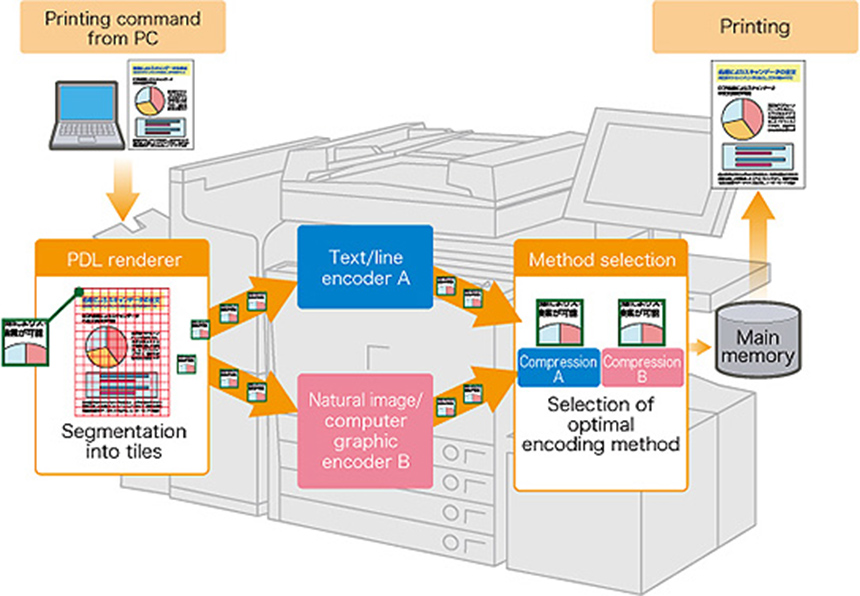
Overview of VL Compression Method
It is difficult for people to notice compression degradation in natural images and complex computer graphics. This means that even if high compression coding is performed on images such as these, they will be recognized as being suitably high quality images. This type of image data is highly compressed using unique Canon compression method suitable for use with natural images and computer graphics.
On the other hand, compression degradation of text or lines in images is very noticeable, an encoding method which produces little degradation must be used. This type of image data is processed using unique Canon compression method suitable for use with text and lines, which produces little compression degradation.
In this way, automatically applying different compression methods depending on the type of image data makes it possible to achieve fast, highly efficient compression.

Comparison of VL and JPEG Image Compression
100MB images compressed to approximately 2.5MB (approx. 1/40thof its original size) using VL compression and JPEG compression. The images compressed using VL compression have a clearly higher image quality than those compressed using JPEG compression.
#Computer science
"MEAP"*8 is an application platform incorporated into Canon digital MFDs. Applications customized to suit users' needs can be run without the use of a PC. MEAP, which realizes independence from the operating system using Java technology, is mainly comprised of three elements; the MEAP platform providing the basic runtime environment, the MEAP system service providing system-related functionality, and the MEAP application.
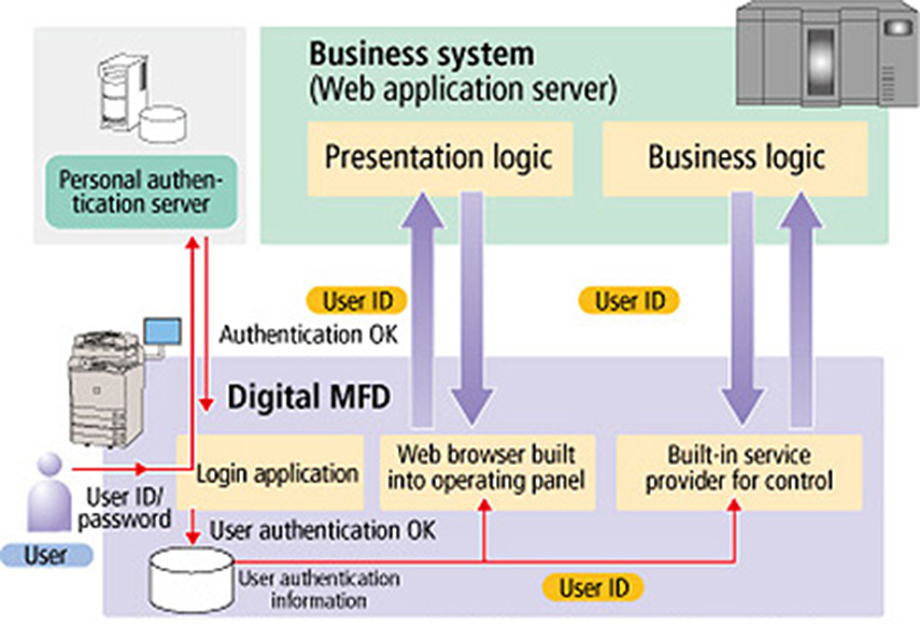
Overview of the Structure of MEAP Web
As the digital MFD performs authentication when connecting to the business system, it is possible to used simple authentication only requiring a user ID when using the system.
"MEAP Connector" is a technology based on MEAP. Business systems for forms, etc., which digital MFDs could not directly output in the past, can now be closely linked to digital MFDs as part of the workflow.
"MEAP Web" makes it possible to call up digital MFD functions from web applications.*9 Web applications and digital MFDs can be operated seamlessly by using the Web browser displayed on the operating panel. MEAP Web contributes to document-related tasks by dramatically improving the links between digital MFDs and Web-based business systems.
#Electrical engineering#Computer science
Producing high-speed, high-resolution output on network digital MFDs creates a heavy load for the printer controller. Canon has developed a printing system that performs optimal data processing for each product and provides efficient high-speed / high-resolution output, without placing excessive strain on the printer controller.
Canon Office MFDs and laser printers incorporate UFR II, developed by Canon for printers. UFR II uses a load-balancing feature to efficiently distribute the processing burden of all components of printer data between the PC and the printer, and also facilitates optimal data processing in line with the printer's RIP*10 capabilities.
UFR II LT, the page description language used in low-cost machines, also uses UFR II technology to carry out PC data processing, enabling high-speed printing even on printers with low processing capabilities.
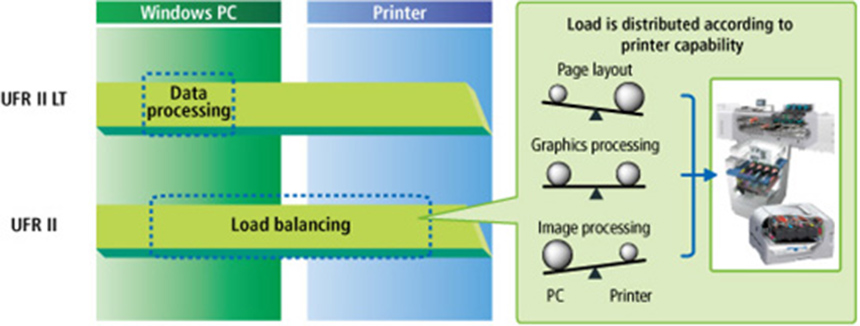
UFR II Load Balancing
In ordinary printers, RIP is processed by software (software RIP). However, in the case of color printers, which handle large volumes of data, it is often impossible to use software RIP for high-speed data processing, meaning that hardware RIP is necessary.
With the aim of enhancing high speed and high resolution of printers, Canon has developed the core technology for high-speed RIP, which can be used as either software RIP or hardware RIP, and will continue to incorporate this into its products. Additionally, Canon is furthering the optimization and parallelization of internal processing in order to accommodate higher speed, and is developing technologies to enable high-resolution data processing by high-speed internal data compression.
#Computer science
Canon Office MFDs do more than just make copies of scanned data. Built-in "document processing technology" enables the creation of reusable electronic documents by analyzing and processing scanned documents.
The first step in document processing technology is document analysis. "Document analysis technology" is used to analyze the layout of a scanned document to extract objects such as texts, diagrams, photographs and graphics, and separate them into their respective areas to generate basic data of each attributes, positions and sizes. These basic data are then processed with character recognition, vector conversion,*11 image processing, and compression by which high-quality documents are created.
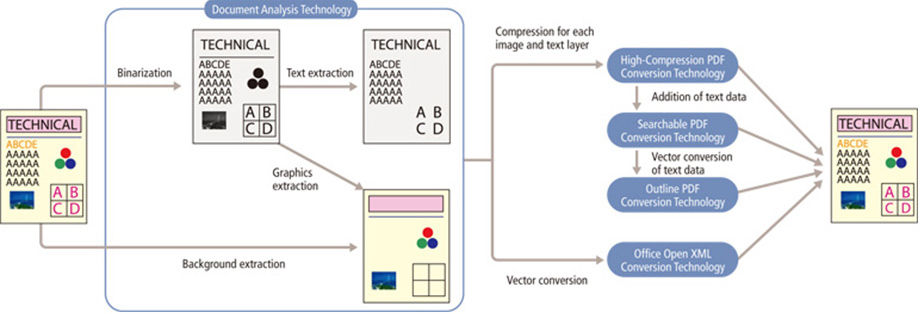
Overview of Electronic Document Creation Based on Document Processing Technology
"High-compression PDF*12 conversion technology" employs document analysis technology to extract text and image data and separate them into multiple layers. This technology enables each layer to then be optimally compressed, providing for a high-compression ratio while maintaining high resolution.
Using conventional compression methods, an A4-size color image scanned at 150 dpi can be compressed to a file size of about 2 MB. With this technology, the same image scanned at a resolution equivalent to 300 dpi can be reduced to roughly one tenth of that size (200KB). Canon is the first company in the world to incorporate this technology into MFDs, and has dramatically improved the capability of handling color document image data, which entails particularly high volumes of data.
"Searchable PDF conversion technology" enables text search within PDF documents by overlaying text, identified and extracted as data using document analysis technology, on the original image as a text layer. The technology achieves a fast processing speed of 7.5 pages per minute for A4-size documents, with a high accuracy rate of 97.75% (based on in-house Japanese-language evaluation samples) .In addition to Japanese, this technology supports English as well as various European and Asian languages.
"Outline PDF conversion technology" represents the evolution of high-compression PDF conversion technology. While this technology conventionally composes text and background data extracted from scanned images, Canon's outline PDF converts text data into vector data and then compresses it to make possible the display of high-resolution text regardless of the resolution of the output devices.
Text and graphics data converted with outline PDF can also be reused in Adobe Illustrator, expanding the range of reusability for scanned documents.

Smooth Text Reproduction in Various Environments
"Office Open XML conversion technology" enables to convert files into the XML-based file format adopted by Microsoft Office 2007. When scanning paper documents, this technology can change text and diagram data into vector data, and convert the documents into PowerPoint format while retaining images, background and layout. This makes it easier to edit text and diagrams compared with conventional PDF conversion, substantially reducing the work required for data input and editing even when the original is a paper document.
#Mechanical engineering#Electrical engineering#Computer science#Physics
Normally, when reading both sides of a document, it has been necessary to flip the document over using a feeder*13 and read each side separately. Optical systems have had complex configurations with scattered parts in the past, and by arranging these into a single unit, Canon made it possible to place scanner units on the feeder side and the platen glass side. This enables simultaneous scanning of both sides of a document in a single pass, resulting in significantly faster scanning. Furthermore, this reduces the risk of damage to documents while scanning caused by paper jams, etc., and also eliminates the operating noise created when flipping documents.
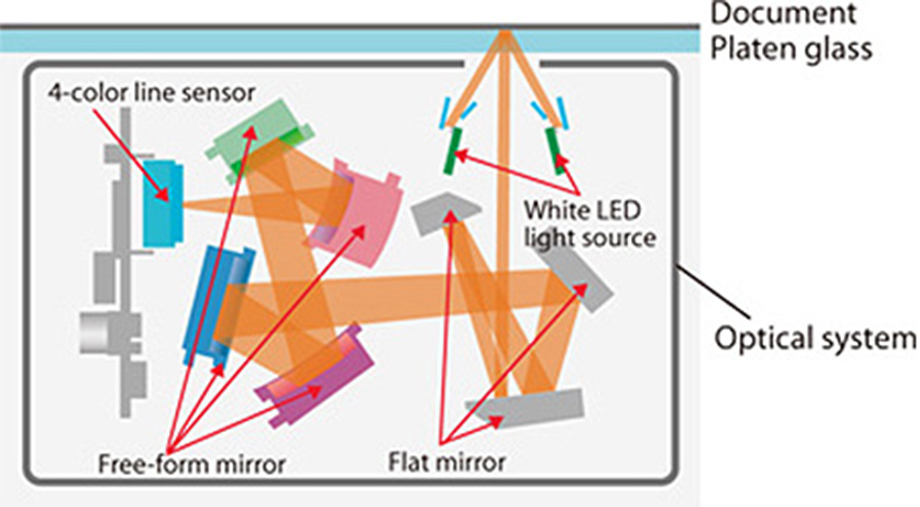
Scanner Unit
This scanner unit utilizes a compact high-performance 4-color line sensor, white LEDs and a proprietary free-form mirror unique to Canon.
The specially designed 4-color inline sensor has a faster data transfer rate than conventional sensors, enabling faster scanning. By using a white LED light source, power consumption has been reduced to one quarter of the level when using a xenon lamp. Furthermore, using a free-form mirror provides a greater depth of field than in the past, making it possible to reproduce a sense of depth when scanning an item with an uneven surface. The optical path length is also 47% shorter, and the scanner unit has been successfully made more compact, this also contributes to reducing the space consumed by Office MFDs.
#Mechanical engineering#Electrical engineering#Physics#Chemistry
Digital MFDs that print using the electrophotographic printing process have required regular maintenance due to wear of the photosensitive drum. Canon has developed a compact long-life drum cartridge to contribute to the reduction of instances of maintenance and the saving of resources.
The E (Excellent) drum incorporated in this system is a photosensitive drum boasting high durability and high stability due to the addition of a layer of specially-developed coating.
The Compact Long-Life Drum Cartridge System utilizes the long-life properties of the E Drum, while adding 3 new mechanisms to ensure it is more compact at a lower cost. The "electrical charging roller cleaning mechanism" reduces contamination and achieves a significantly longer lifetime by adding a cleaning component to the electrical charging roller. The "cleaner pre-exposure mechanism" contributes to providing a more compact size at lower cost by using an LED as the light source for removing residual charge from the photosensitive drum after exposure. Furthermore, the "toner removal cleaner mechanism" reduces abrasion of the photosensitive drum by not fixing the cleaning blades in place.
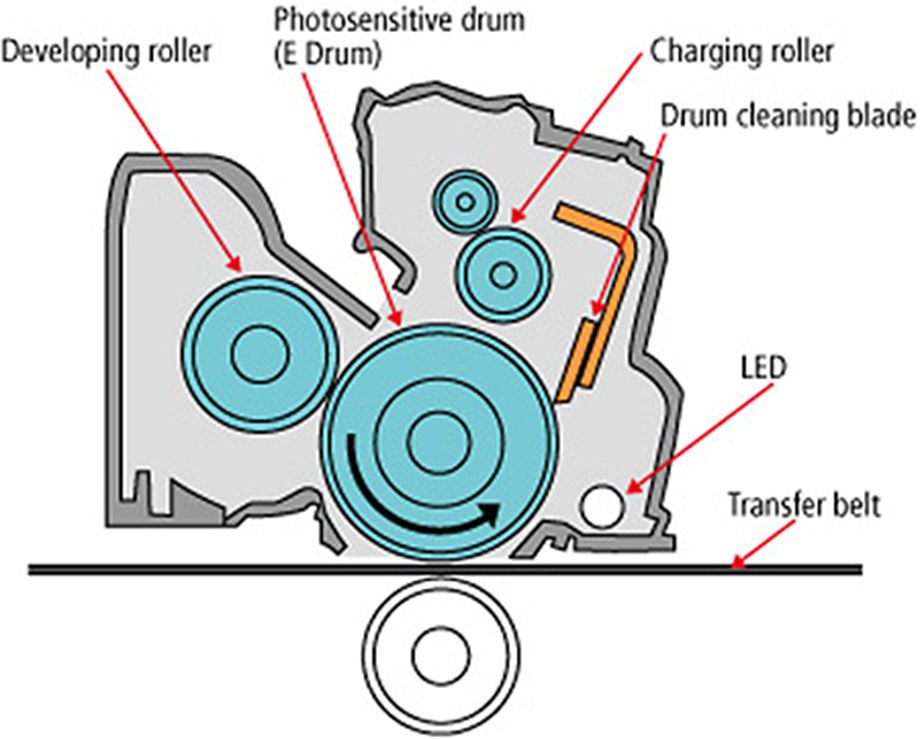
Compact Long-Life Drum Cartridge System
#Chemistry
Canon utilizes CV toner, which features optimized melting properties while maintaining highly precise pigment dispersion. This ensures consistent colors even during high-volume printing and makes possible excellent color reproduction that rivals that of offset printing. The toner also boasts superior transfer performance and durability to reduce image roughness when printing on various types of media. CV toner enables high-resolution, vivid image quality to be maintained for a longer period of time.