News Release
May 29, 2023
Canon Inc.
Canon develops perovskite quantum-dot inks for use in next-generation displays, with improved durability and potential for application in high-image-quality displays
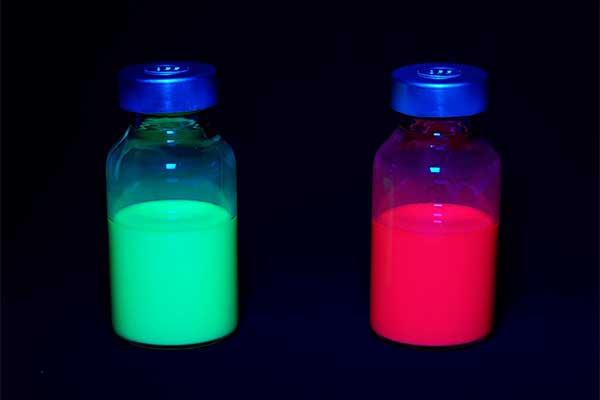
TOKYO, May 29, 2023—Canon Inc. announced today that the company has developed a quantum-dot ink with a perovskite structure (perovskite quantum-dot ink) as a material for next-generation quantum-dot displays, and has successfully demonstrated its practical durability1 for the first time2 in the world.

The performance and image quality of display devices continue to rapidly improve, and towards this end, one such approach that is gaining momentum is applying quantum-dot technologies (QD) to meet the need for displays with higher image quality.
Quantum dots are semiconductor nanocrystals that measure only a few nanometers in diameter and can emit light with high brightness and high color purity. Displays with quantum-dot technology are attracting growing attention due to their wide color gamut that makes possible high visual expressiveness. Therefore, quantum dots for display is sought to achieve higher color purity and higher light utilization efficiency. In addition, though cadmium (Cd) has thus far been the preferred material for quantum dots, due to environmental concerns, there is a growing interest in Cd-free materials.
With these requirements in mind, Canon has focused on the development of perovskite quantum-dot inks. Perovskite quantum dots are considered an effective Cd-free approach other than InP (indium phosphide) quantum dots. In terms of color purity and light efficiency, many see perovskite quantum-dots as a promising material capable of contributing to high brightness, a wide color gamut and high resolution. However, poor durability has thus far been a barrier to practical use.
To address the issue of durability, Canon is leveraging its proprietary technologies nurtured through development of ink and toner for printers. The company has established a unique method to form a protective shell on quantum dots, thereby achieving practically durable perovskite-dot ink with retained color purity and light usage efficiency.
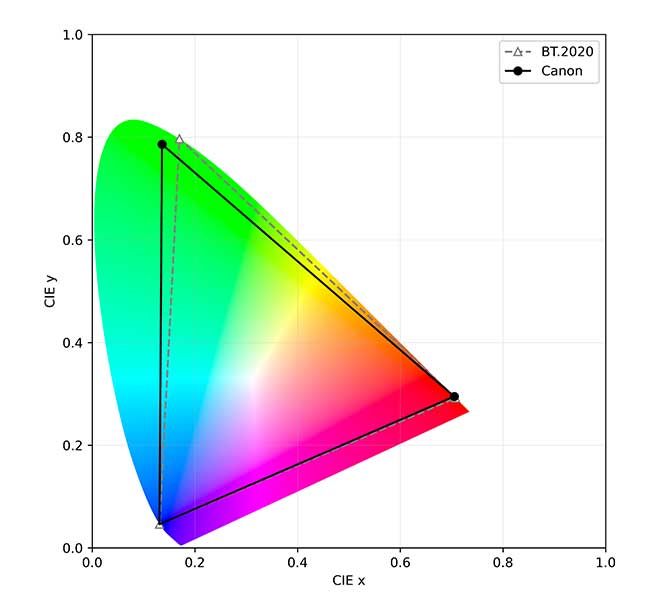
InP quantum-dot ink covers 88% of the color gamut based on the ITU-R BT. 2020 recommendation3, while Canon's perovskite quantum-dot inks can cover 94%4 of the gamut. In addition, the high efficiency of light use is expected to reduce power consumption of quantum dots by approximately 20%5 compared to conventional technology.
Canon’s quantum-dot inks have the potential to help realize next-generation OLED displays with ultra-high definition, such as quantum-dot 8K displays, a technology that thus far has been unachievable.
The results of technological development of the ink and the technology for mass-production of high-quality perovskite quantum dots were announced on May 26, 2023 (local time) at SID Display Week 2023 in Los Angeles, USA.
- 1
T90=10,000 hours. The time until the brightness reaches 90% of the initial value at 1,000nit (a unit indicating the degree of brightness), which is equivalent to the blue light brightness under actual use.
- 2
As of May 28, 2023. Based on Canon research
- 3
Recommendation formulated by ITU (International Telecommunication Union) to provide video signals for UHDTV broadcasting systems
- 4
Estimation when a display is constructed by combining a red/green ink-cured film with an appropriate blue light source
- 5
Estimation when used in current OLED TVs utilizing quantum dots
Canon‘s perovskite quantum-dot inks
- Quantum-dot ink with indium phosphide cover 88% of the color gamut based on the ITU-R BT. 2020 recommendation, while Canon's perovskite quantum-dot inks can cover 94%4 of the gamut.
- Canon’s quantum-dot inks have the potential to help realize next-generation OLED displays with ultra-high definition, such as quantum-dot 8K displays, a technology that thus far has been unachievable, thanks to the high conversion efficiency of light that makes possible smaller pixels.
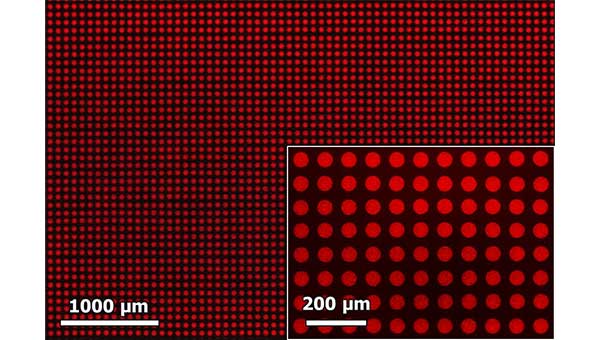
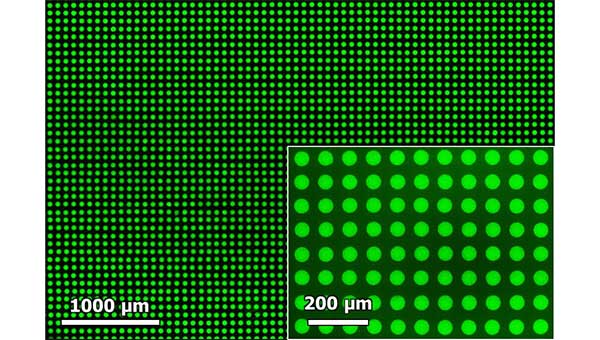
High resolution print samples of the perovskite quantum-dot inks
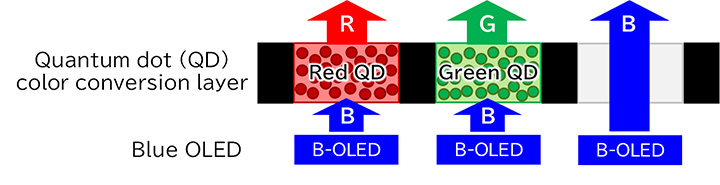
OLED displays using quantum dots
- Quantum dots convert the blue light of the light source into red and green. Compared with white light sources, quantum-dot technology makes possible red and green light with higher color purity, thus enabling displays with a wider color gamut.
Perovskite quantum dots
- The wave length (color) of emitted light can be controlled by compositions and particle sizes of perovskite quantum dots.

What is a perovskite structure?
A perovskite structure is one type of crystalline structures. By changing the elements that compose a perovskite structure, a variety of properties can be manifested, including superconductivity, ferroelectricity, fluorescence and photoelectric conversion. Due to this versatility, a perovskite structure holds great potential for use as functional materials. In recent years, perovskite solar cells have attracted attention thanks to their low cost and versatility that enables them to be used anywhere.
Enquiries
- General Enquiries
Please include the keyword "perovskite quantum-dot ink" in the email subject line.
