Innovating Together
At Canon, we define open innovation as the pursuit of discovering technologies within universities and research institutions — technologies that have the potential to become future business drivers or contribute to solving societal challenges. By leveraging Canon’s technological strengths, we aim to bring these technologies to practical applications and create new values for society.
Our initiatives include a wide range of activities that foster value creation: providing research grants for scientific and technological advancements through the Canon Foundation, participating in national research and development projects related to cutting-edge semiconductors and iPS cells, and engaging in joint research with external partners.
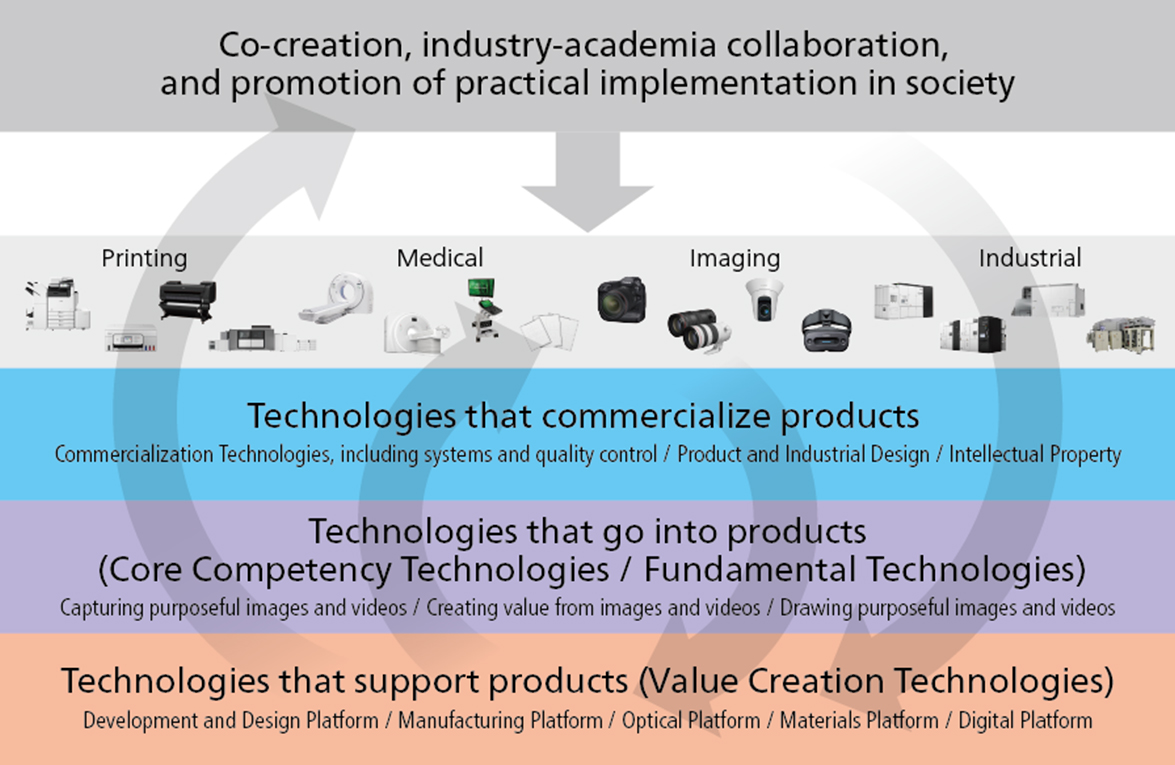
Canon's Platform for Open Innovation
Canon’s technology platform, which consists of three technological foundations, is not just a collection of individual technologies, but a systemized environment that is utilized throughout the company and across the business boundaries.
This unique technology platform is what makes it possible for the company to grow across its four industry-oriented group. This same environment also supports new ventures—whether they join through mergers and acquisitions or through partnerships with universities and research institutions. By making it easy to apply Canon’s core technologies, it helps these new projects move forward quickly and reach their goals sooner.
As new products are developed and produced within this environment, the technologies gained and refined in the process are fed back into core technological foundations. Through this ongoing cycle of innovation and improvement, Canon’s technologies continue to grow stronger and evolve—paving the way toward the future.
The Canon Foundation
Through the Canon Foundation, Canon supports scientific research aimed at solving social challenges and driving innovation for the future. The Foundation provides grants to researchers who envision new forms of value for society and boldly explore the unknown frontiers of science and technology needed to realize that vision. To help turn as many of these ideas as possible into real-world solutions, Canon actively engages with researchers and explores how its core technologies can support their efforts.

Application case study:
Development of technology to manufacture advanced semiconductors for post-5G use
Through participation in R&D projects led by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry of Japan, Canon is working to develop manufacturing technologies for advanced semiconductors that will be needed in post-5G communications.
Compared to the 4th Generation Mobile Communication System (4G), the 5th Generation Mobile Communication System (5G) is more advanced, and commercial services have started in a number of countries. Based on 5G but offering even stronger functionality, post-5G is expected to become a core technology for Japan’s competitiveness and is likely to be used in various industrial applications, such as autonomous driving, which is enabled by minimized latency, and smart factories, which can be realized thanks to a large number of simultaneous connections.
The nanoimprint (NIL) semiconductor manufacturing equipment currently being produced by Canon is based on a principle different from that of conventional equipment and enables semiconductor patterning—the process of forming minute circuit patterns on a semiconductor substrate—at lower production and investment costs. The equipment is expected to help reduce production costs for the advanced semiconductors required for post-5G communications.
Through this project, Canon will promote the development of nanoimprint lithography (NIL) semiconductor manufacturing equipment for advanced semiconductors and verification of processing on a prototype line in collaboration with the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, aiming to contribute to further miniaturization of semiconductors and establish low-cost semiconductor production technology.

Application case study:
Photon counting computed tomography
Photon counting computed tomography (PCCT) is the next generation of computed tomography (CT). This is a technology in which each photon (the smallest unit of light) is counted. As the photons are individually identified, energy information can be obtained for each photon. As noise can be eliminated from the image, the exposure dose required to generate a diagnostic image can be reduced and high-resolution images can be obtained with lower exposure doses than those required by conventional CT. It is also expected that the acquired energy information will be useful for accurate determination of the malignancy of tumors in the body.
In PCCT, the capability of the detector that receives X-rays affects image quality. In 2021, Canon welcomed Canadian semiconductor manufacturer Redlen Technologies Inc. to the group, acquiring mass production technology for semiconductors made of cadmium, zinc, and telluride compounds (CZT). This ensures that Canon will remain on track for implementation of the CZT semiconductor detectors used in PCCT.
The newly developed CZT semiconductor detector has improved X-ray detection efficiency, and optimized the unique compact detector circuitry as well as pixel size for improved resolution, allowing generation of low-noise, high-resolution images.
Canon aims to commercialize its unique PCCT technologies through synergy between Canon technologies developed for conventional CT systems and the newly developed CZT semiconductor detector. These technologies include X-ray tube design, vibration suppression mechanisms for gantries and patient couches, high-capacity data management and transmission systems, deep learning reconstruction technology, etc. Canon is currently conducting clinical research in collaboration with four advanced medical research institutes in Japan, the United States, and Europe, and will contribute to more accurate and efficient diagnosis while minimizing the burden on patients.

Application case study:
Production of artificial platelets using iPS cell culture systems
Canon is participating in an R&D project to artificially produce high-quality platelets from iPS cells. This project is part of the Key and Advanced Technology R&D through Cross Community Collaboration Program led by the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), a national research and development corporation. Seven organizations are involved, including the Center for iPS Cell Research and Application of Kyoto University (CiRA).
Platelets play a crucial role in blood clotting during hemostasis, the process that stops bleeding. However, platelets have a short life of only about four days, and long-term storage is not possible. Therefore, as platelets are a donor-dependent blood product, it can be difficult to secure sufficient platelet supply in emergency situations, such as disasters in which a large number of people with serious injuries require platelet transfusion.
This project aims to address such challenges by establishing a practical system to artificially produce platelets from iPS cells in order to ensure the stability of this important medical supply. If a process to artificially produce platelets can be achieved, it will help speed up emergency medical care for many patients, such as disaster victims suffering from massive bleeding and severe trauma.
To expand the scope of its medical business, Canon has started development of a cell processing system which will be used for regenerative medicine. The goal is to create cell processing systems that can stably mass produce cells by applying technologies it has acquired over the years through the development and production of medical systems. In this project, Canon will be responsible for the development of cell processing systems necessary for processes such as cell culture, concentration/purification, and filling,* and will contribute to the development of emergency medicine by promoting R&D activities for the practical application of cell processing technology.
- *: Dividing cells after adjusting the concentration of the cells according to a single dose to the patient.

Related Links
R&D introduction PDF "THE CANON FRONTIER"
Technology