Technology in ProductsSputtering Equipment
Vacuum thin-film deposition equipment essential for semiconductor manufacturing
With the rapid advancement of generative AI, demand for semiconductor devices—especially those used in data centers—is increasing. Sputtering equipment supports semiconductor manufacturing by enabling high-quality, high-precision film deposition using advanced vacuum technologies.
December 2, 2025

How sputtering equipment works
What is sputtering equipment?
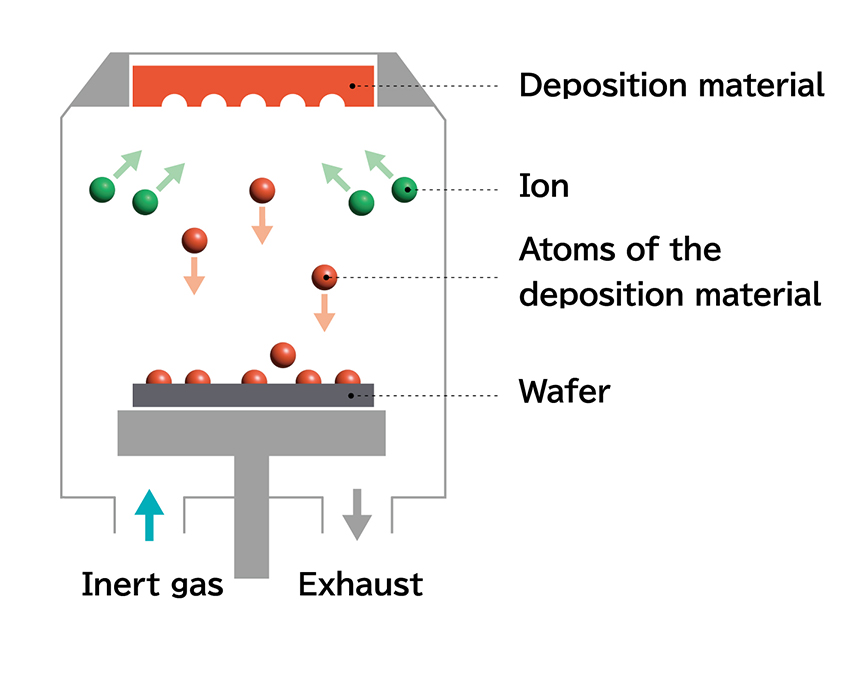
Sputtering equipment is used to form thin films on a wafer to create circuits for semiconductor devices. It is typically used in the production of Semiconductor devices, which are seeing growing demand in fields such as generative AI and the automotive industry.
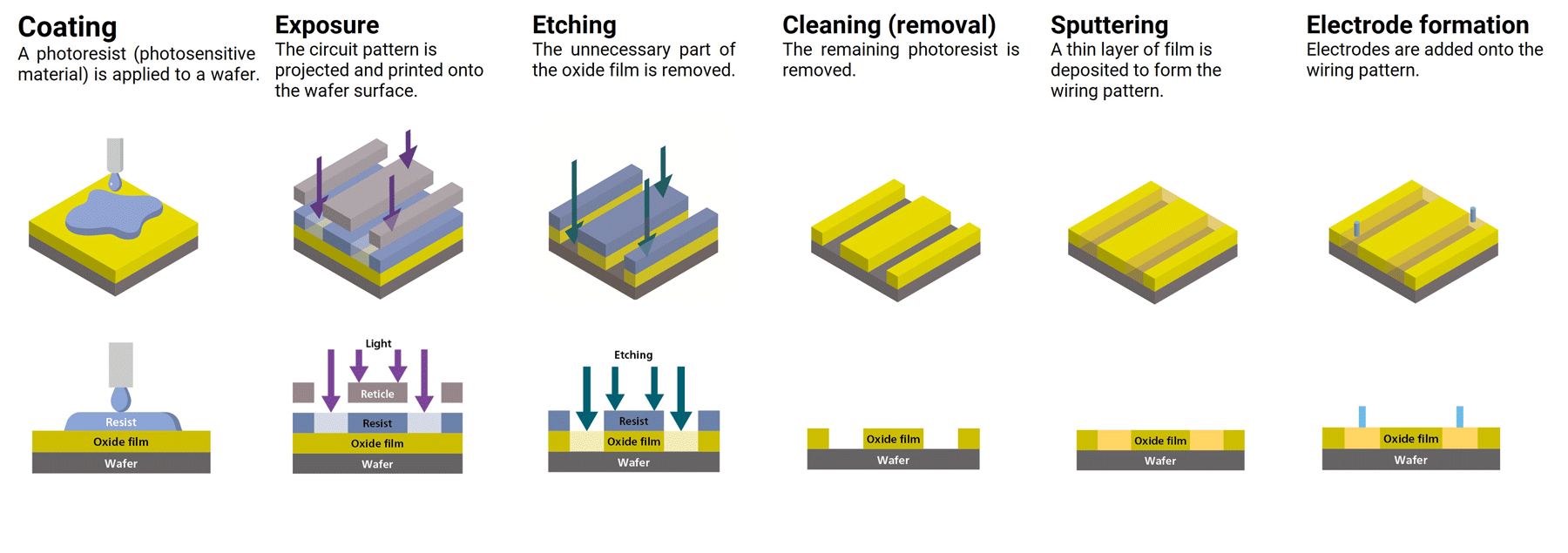
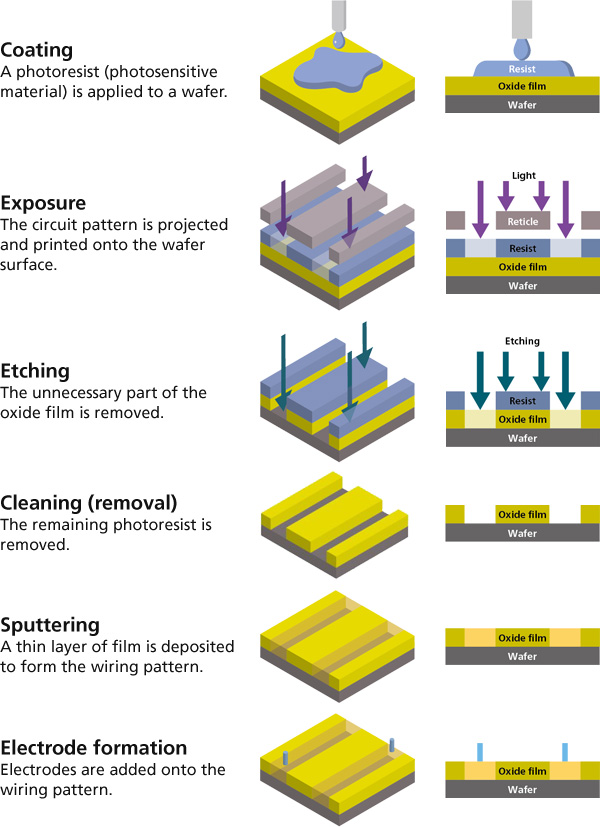
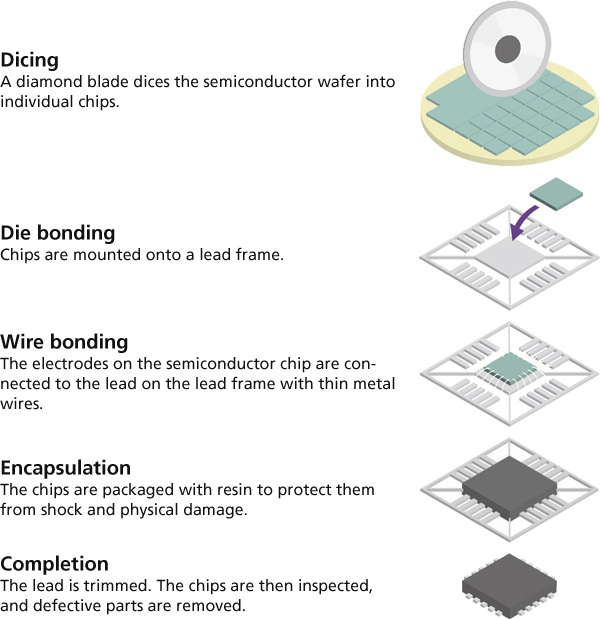
The manufacturing process of semiconductor chips is divided into two stages: the front-end process, where electronic circuit patterns are formed on a wafer, and the back-end process, where the patterned wafer is cut into individual chips and assembled to function properly within electronic devices.
Among the various semiconductor manufacturing systems, sputtering equipment is primarily used in the front-end process to deposit thin films onto the wafer. A single semiconductor chip may contain over thirty
layers of film, with each layer requiring highly precise deposition technology—some as thin as 1 nanometer (nm), which is one-billionth of a meter.
[Front-end processing]
[Back-end processing]

Read More
Canon’s Sputtering Technology
Oblique sputtering with rotating substrate: A technology for uniformly forming ultra-thin films of less than 1nm
Oblique sputtering with rotating substrate is a technique in which the cathode electrode that generates plasma is positioned at an angle to the wafer
surface, and the substrate stage rotates during film deposition. This allows for uniform film formation and precise control of film thickness, enabling the creation of extremely thin films. Multiple pieces of target material
can also be arranged, making it possible to build films with over thirty layers
using different materials.
This technology contributes to the production of various semiconductor devices, including non-volatile memory* that supports energy-efficient operation.
* Memory that retains data even when the power is turned off, such as USB flash drives, SSDs, and contactless IC cards
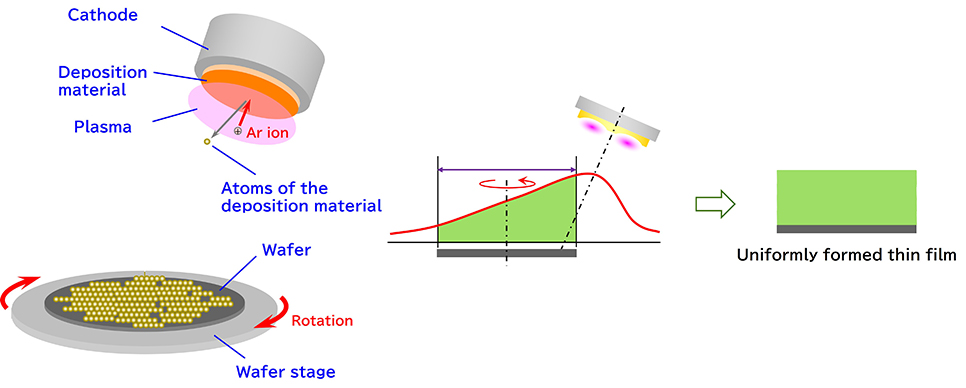
Uniformly formed thin film
Application to atomic diffusion bonding technology
In semiconductor device manufacturing, technologies that enhance performance by bonding wafer together are advancing. Canon’s atomic diffusion bonding system enables this by utilizing sputtering technology to form a thin bonding layer on the surfaces of the wafer.
During bonding, atoms at the interface rearrange themselves according to the atomic structure of the opposing surface—a phenomenon known as atomic diffusion. This results in a bond so strong that the boundary between the materials becomes nearly indistinguishable.
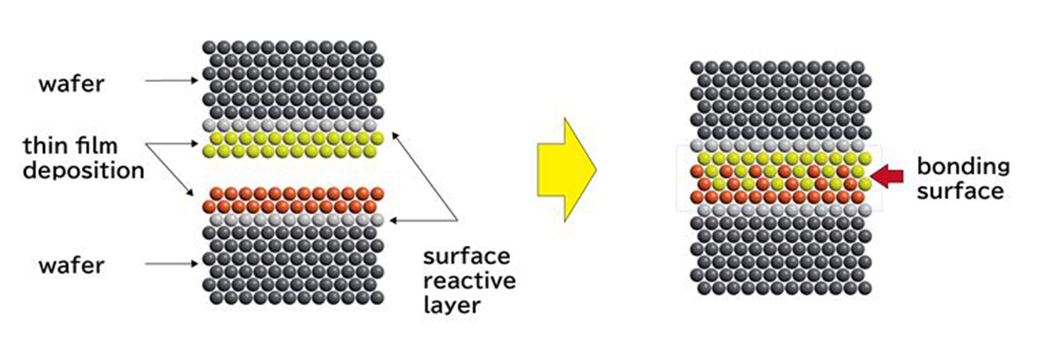
Right: Robust bonding achieved through atomic diffusion
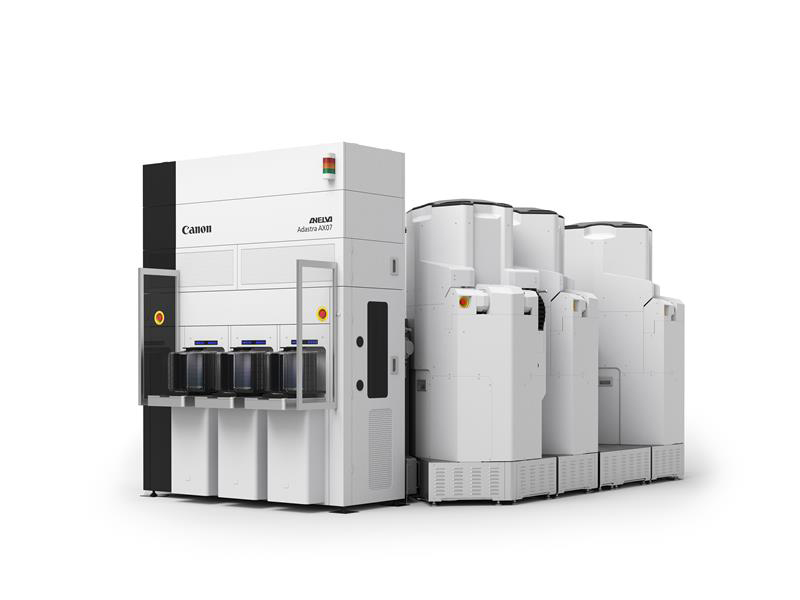
(Column) Adastra: Winner of the 2024 Good Design Gold Award
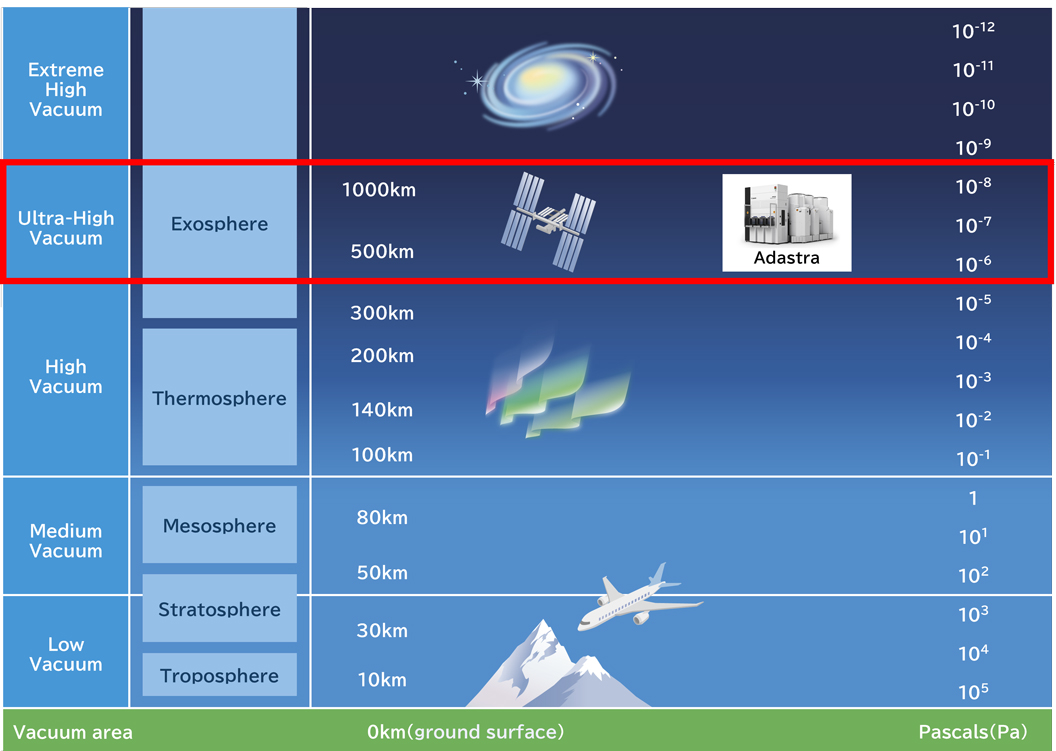
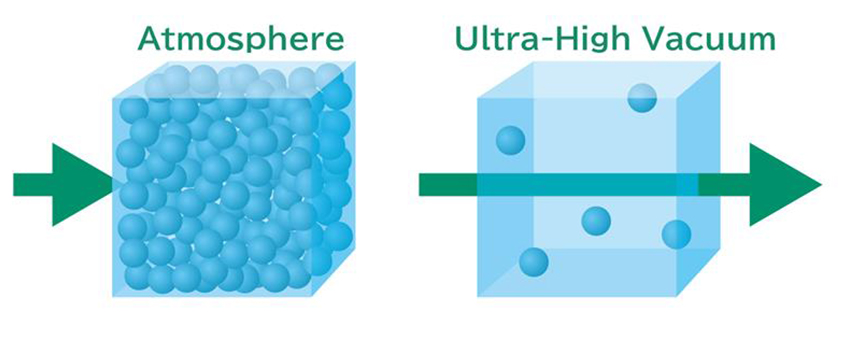
Adastra is a sputtering system that offers flexible configuration options tailored to the semiconductor devices being produced, allowing it to meet a wide range of needs. In the semiconductor industry, where both productivity and environmental considerations are essential, Adastra enables nano-level thin film deposition while minimizing space and energy consumption.
Its design and usability have been highly praised, earning it the Gold Award in Japan’s 2024 Good Design Awards and the top prize (Minister of Economy, Trade and Industry Award) at the 55th IDEA Machine Industry Design Awards. Internationally, it also received the Gold Award at Germany’s 2025 iF Design Awards in recognition of both its technological excellence and design quality.


Click here to learn more about the “Adastra” sputtering equipment series for semiconductors and electronic components