Chemical Substances / Pollution Prevention
Management of Chemical Substances used in Manufacturing Processes
The chemical substances handled during manufacturingat Canon include "controlled chemical substances" regulated in terms of safety such as negative impact on human health, the environment, and flammable risk. Canon categorizes these substances and has put effective measures in place for each category.
List of Controlled Chemical Substances
| Rank | Explanation |
|---|---|
| A | Substances specified by the Chemical Weapons Convention, the Stockholm Convention, the Montreal Protocol and the Convention concerning Safety in the Use of Asbestos, as well as specified greenhouse gases (PFCs/HFCs/SF6), other soil and groundwater pollutants, and substances that significantly impact people's health |
| B | Greenhouse gases other than PFCs/HFCs/SF6 , greenhouse gases whose global warming potential (GWP) has been determined by the IPCC, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and other substances designated by Canon |
| C | Chemical substances with defined compliance requirements, including compliance with reference values and the ascertainment of usage and storage quantities |
Reducing Use and Emissions of Controlled Chemical Substances
Canon engages in various initiatives at its operational sites to reduce emissions of controlled chemical substances, including reducing the volume of substances used by improving production processes and reusing the substances. In 2024, Canon Dalian Business Machines took steps to reuse and recycle solvents, as did Canon Inc., Taiwan, amid other efforts to replace controlled chemical substances with other substances.
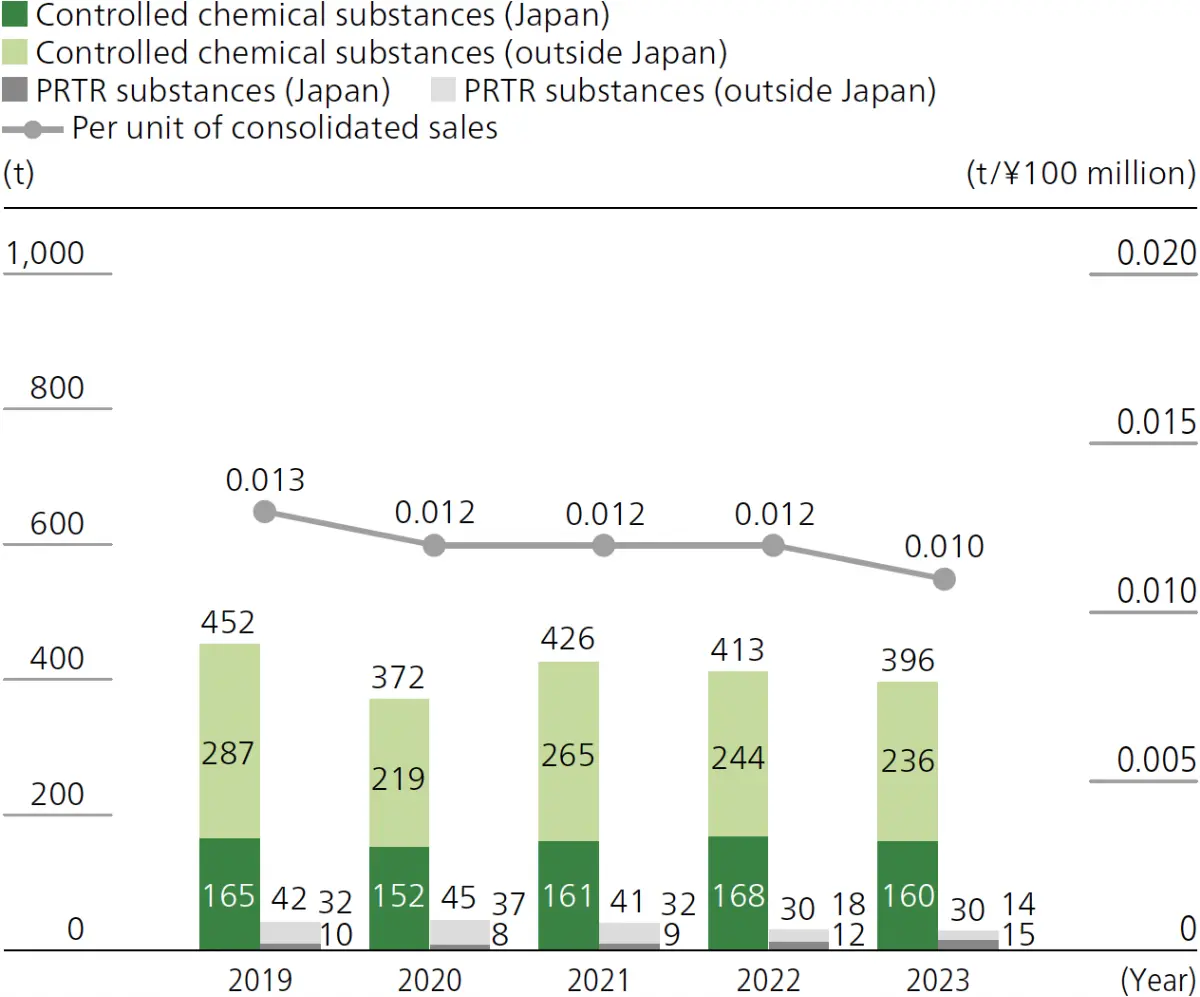
- * PRTR System: Pollutant Release and Transfer Register System, a notification system for the transfer and release of chemical substances.
- * Controlled chemical substances exclude regulated substances.
- * The scope of aggregation mainly includes companies that have acquired ISO 14001 consolidated certification.
Reducing Emissions into the Atmosphere and Waterways and Preventing Pollution
Canon alleviates the environmental impact of its operational sites by reducing emissions of NOx*1 and SOx*2, which are major causes of air pollution and acid rain; reducing discharge of phosphates and nitrogen compounds, which cause the eutrophication of water environments; and, reducing BOD*3 and SS*4, which indicate an environmental impact in water areas. One example of this is Canon Components, the first member of the Group to introduce a new treatment process to reuse the active carbon contained in waste sludge. By removing the small residue of ink in treated wastewater, this process realizes reduced environmental impact.
To prevent air pollution, when installing or updating equipment that uses fuel, we opt for fuels that minimize generation of air pollutants (such as sulfur oxide, nitrogen oxide and soot), and have banned the use of heavy oil in principle. Furthermore, we have designated ozone-depleting substances and persistent organic pollutants cited in the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants as banned substances. With regard to wastewater, each operational site sets standard values based on local laws and regulations. Also, control values are set at 80% of the standard values as management standards at each site.
We regularly check the status of compliance with management standards.
- *1 Nitrogen oxides (NOx) A major cause of air pollution, acid rain and photochemical smog, NOx is generated when the nitrogen in fuels is oxidized or when nitrogen in the atmosphere is oxidized during high-temperature combustion.
- *2 Sulfur oxides (SOx) A major cause of air pollution and acid rain, SOx is generated when fossil fuels, such as oil and coal, are burned.
- *3 Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) BOD is the amount of oxygen consumed when microorganisms degrade organic matter in water. Larger figure indicates worse water quality.
- *4 Suspended solids (SS) A collective term used for substances of less than 2 mm in diameter that float in the air and do not dissolve.
Chemical Substance Reduction in the Semiconductor Device Pretreatment Process
Some 30% of the semiconductor treatment process consists of cleaning the wafer (semiconductor element material) with various chemical substances. These substances are replaced at regular intervals regardless of how long the equipment has been in operation for. The semiconductor device manufacturing facility at Canon's Ayase Plant has developed a predictive tool that tracks the constantly changing situation on the production line together with data on production plans, maintenance, and the facility's capacity, allowing phased operation of equipment. By setting facilities to shut off for planned periods, the plant has reduced the frequency of replacement of the chemical fluids and thereby cut down on the total amount used. A yearly saving of around 23,000 liters of chemical substances is expected.
Soil and Groundwater Management Status
Canon places high priority on soil and groundwater protection. In line with this, we established the Canon Group's Basic Policy on Soil and Groundwater Pollution and implement comprehensive measures based on it. In the unlikely event that soil or groundwater pollution is found at one of our operational sites, cleanup and remedial actions are carried out in close accordance with all relevant laws.
Canon has also adopted an internal standard for acquiring new land, conducting a preliminary soil examination and carrying out any other necessary procedures, such as soil remediation, before making the purchase. We also monitor the chemical substances used at each site and, considering applicable national and regional standards, develop risk countermeasures according to the local situation.
Status of Soil and Groundwater Clean-up Activities*
| Operational Site | Substances | Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Shimomaruko | 1,2-dichloroethylene | Injection of treatment agents, water quality measurement |
| Utsunomiya parking lot 1 | Fluorine and its compounds, etc. | Pumping, water quality measurement |
| Toride | Trichloroethylene, etc. Hexavalent chromium and its compounds | Covering, pumping, water quality measurement |
| Canon Ecology Industry | Trichloroethylene, 1,1-dichloroethylene | Covering, pumping, water quality measurement |
| Canon Components | Mercury and its compounds | Covering, water quality measurement |
- * Reports are made to the authorities concerning sites where remediation is in progress.
Going forward, we will continue with the above initiatives and carry out monitoring and reporting of operational sites with completed remediation in a timely manner.
PCB Waste Management
In accordance with relevant laws, Canon strictly manages polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB), which damages living organisms and the environment. As of December 2024, no operational sites stored highly concentrated PCB waste.
