Climate Change
Initiatives to Large-Scale Natural Disasters
Mitigation measures to lower emissions of CO2 and other greenhouse gases are important in minimizing the effects of climate change as much as possible, but adaptation measures are also needed at the same time to prepare for any impacts that cannot be mitigated.
Trial of Smart Agriculture that Aids Adaptation to Climate Change
As a way of helping agriculture to adapt to the environmental changes caused by climate change and other factors, Canon has used its many years of experience in imaging technology to develop the GM-1 crop growth monitoring system, a non destructive, non-contact tool that uses images of crops to provide automatic access to growth metrics. We are now engaged in a trial of the system in paddy rice cultivation.
GM-1 combines Canon's unique image analysis technology, adapted to crop characteristics, with AI diagnostic technology based on deep learning. Through its capacity for data accumulation and comparison with past data, the system is expected to find applications in areas such as crop adaptation to climate change, optimal cultivation management, and development of new crop varieties.
Contributing to Climate Change Adaptation Based on Hydroponic Plant Factories
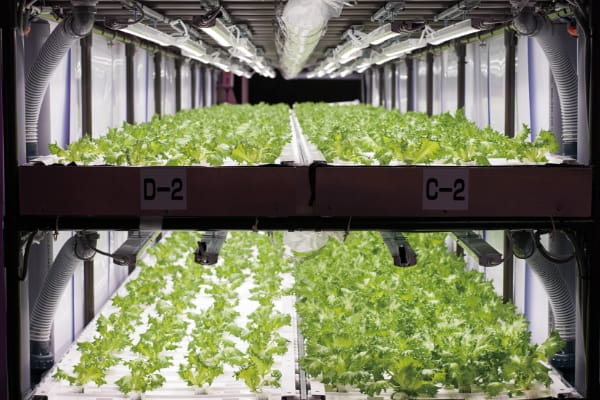
Food supply risks are increasing due to the higher climate change-related incidence of flooding and droughts. Hydroponic plant factories, which can provide a stable supply of crops even in urban areas under climate-independent conditions, are drawing attention as an example of adapting to climate change. Locating production in the cities that are the major areas of consumption also enables lower CO2 emissions from food transportation. Indoor crop cultivation can also be advantageous due to a lack of pests, helping to significantly cut the use of fertilizers and other chemicals such as disinfectants. However, managing growing conditions and establishing a production framework requires know-how, and many processes must be done manually, making labor costs a major issue.
With strengths in automation technology, Canon Electronics is developing equipment to automate the various manual processes used in hydroponic-based plant cultivation with the aim of boosting production yields. The company is also developing software to control the temperature, humidity and other growing conditions, with the long-term aim being to create an unmanned plant factory.

Comment from Plant Factory Staff

I was responsible for mechanical design. The culture at Canon Electronics is to make everything in-house, but I was repeatedly surprised and excited at how we began with the cultivation panel concept and managed to create the mold design, in-house molding and automated equipment. (Toru Takahashi, Precision Equipment Design)
I worked on the conditions for cultivation. I can never forget my joy at finding the best conditions to enable reliable harvesting. We had to persevere to satisfy the strict demand of the person designing the harvester, who insisted that the crop's outer leaves stand up so the cutting point would be easy to see. (Yuuki Kanzou, Materials Research)
Disaster Monitoring with Network Cameras
Because Taiwan is plagued nearly every year by flooding caused by powerful typhoons and heavy rain, causing crop damage and posing a danger to people, a Hydrological Conditions Instant Video Surveillance System has been introduced. Surveillance cameras were installed along the southwestern coastal areas to monitor flood-warning levels and automatically sound alarms as the possibility of a flood increases.
AXIS 214 PTZ Network Cameras and AXIS Camera Station video management software are being used at 150 hydrological sites throughout Taiwan in order to monitor changes in water level with a 360° range, 24 hours a day.
Adaptive Measures at Operational Sites to Deal with Climate Change
Miyazaki Canon site
In some regions, an increase in abnormal weather patterns has increased the risk of flood damage. We have already begun implementing appropriate responses to climate change. In Japan, for instance, we have relocated the Miyazaki Canon site, replacing the former riverside structures with new buildings on higher ground. Similarly, at our Thai production base, we used an elevated site to build Plant No. 2. Going forward, we will continue our progress with the formulation and updating of risk response plans to increase resilience.


