History
The history of Canon's intellectual properties in the medical field
Medical
-
1940Patent activities supporting the X-ray camera business
The Precision Optical Industry, Co., the predecessor of Canon Inc., delivered Japan's first X-ray indirect camera CX-35 to the Navy in 1940 and launched it in the following year. CX-35, which was designed for mass screening purpose using 35mm camera films, is a memorable product marking our entry into the medical equipment market.
The oldest of Canon's intellectual property rights related to X-ray imaging is - to the best of our knowledge - Utility Model No. 337330 (Examined Utility Model Publication No. S18-008498). Since then, Canon has been filing more than 2,500 patent applications in this field. The figure of "2,500" is clear proof that our patent activities have been supporting the X-ray camera business of the Medical Equipment Business Group very well.
CX-35 (launched in 1941) 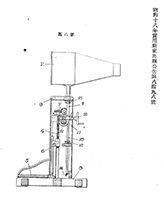
Drawing from Utility
Model S18-008498 -
1976The world's first non-mydriatic retinal camera was launched
In 1976, Canon launched the world's first non-mydriatic retinal camera CR-45NM. With the non-mydriatic technique, we can observe the retina with near-infrared light and can capture its color image with a visible flash light through a pupil naturally dilated in a dark room. Thanks to this technique with no drug, the pupil contracts immediately by the flash light as a natural reaction, so non-mydriatic cameras are now commonly used for early detection of hypertension and diabetes in a general health check-up. Focusing and alignment technologies with near-infrared light invented by Canon are fundamental ones that have been passed down to the majority of non-mydriatic cameras currently on the market.

CR-45NM (launched in 1976) -
2002Brand-new design of fully automatic non-contact tonometer was launched
A non-contact tonometer is a device to measure intra-ocular pressure by detecting a cornea deformation caused by an air puff toward the eye. As the name suggests, the device never comes into contact with a patient's eye to reduce an infection risk and measurements can be done without anesthetics. On the other hand, first-time patients and children may become nervous during the examination since the air puff gives a slight impact which is not experienced in normal life.
In order to solve this problem, Canon's designer utilized novel elements of shape and color to create a less visually oppressive design, taking into account the usage and psychological aspects, achieved by a tight communication with R&D and intellectual property staff. As a result, TX-F was awarded the Good Design Award in 2003.
Fully automatic non-contact tonometer: TX-F (launched in 2002) -
2003Next generation portable X-ray digital camera was launched
Our portable X-ray digital camera CXDI-50G launched in 2003 had the widest field of view in the industry at that time. Canon's original flat-panel sensor gave it a thinner body and lighter weight and enabled flexible photography of an affected portion from any direction.
In terms of design detail, its rounded shape gives a soft impression to relax the patient and its improved operability helps doctors and technicians in their daily work. CXDI-50G's successful and unique industrial design, expressing both gentleness and reliability, was protected by a design registration and was awarded the Good Design Award in 2004 as well.
CXDI-50G (launched in 2003) -
2005Digital X-ray sensor patent was awarded the Imperial Invention Award
Starting from the development of the world's first digital X-ray camera (CXDI-11) launched in 1999, Canon has been aggressively filing numerous patents related to digital X-ray imaging.
It deserves special mention that Patent No. 3066944, the refresh driving technology of MIS (Metal-Insulator-Semiconductor) type sensors, was awarded the Imperial Invention Prize (onshi hatsumei shou in Japanese), the highest prize of the National Invention Award, in 2005 (the second time in Canon's history that we received this honor). The committee commended that it made a significant contribution to the spread of digital radiography.
Intellectual Property History
by business field
-
Printing
The history of Canon's intellectual properties in the printing field
Read more

-
Medical
The history of Canon's intellectual properties in the medical field
Read more

-
Imaging
The history of Canon's intellectual properties in the imaging field
Read more

-
Industrial
The history of Canon's intellectual properties in the industrial field
Read more

