Supply Chain Management
Initiatives
Initiatives with Suppliers
Supplier Evaluation
Before starting business dealings with a new supplier, Canon conducts an assessment based on the Canon Sustainability Supplier Guidelines and other reference standards of whether the company fulfills all requisite standards in terms of corporate ethics, environmental conservation (chemical substance management, prevention of air pollution and water pollution, proper disposal of waste, initiatives aimed at conserving energy and resources, reduction of GHG, and biodiversity conservation), finance, and production structure. Only those suppliers who meet these criteria are accepted as suppliers. We aim to preferentially deal with suppliers evaluated highly in our comprehensive assessment including our annual supplier survey as well as each supplier's trade performance. In addition, we conduct on-site audits of suppliers with low evaluations, providing guidance and instruction for improvement. In particular, Canon may choose to terminate business with suppliers if they are not complying with laws and social norms covering areas such as human rights, labor, and the environment.
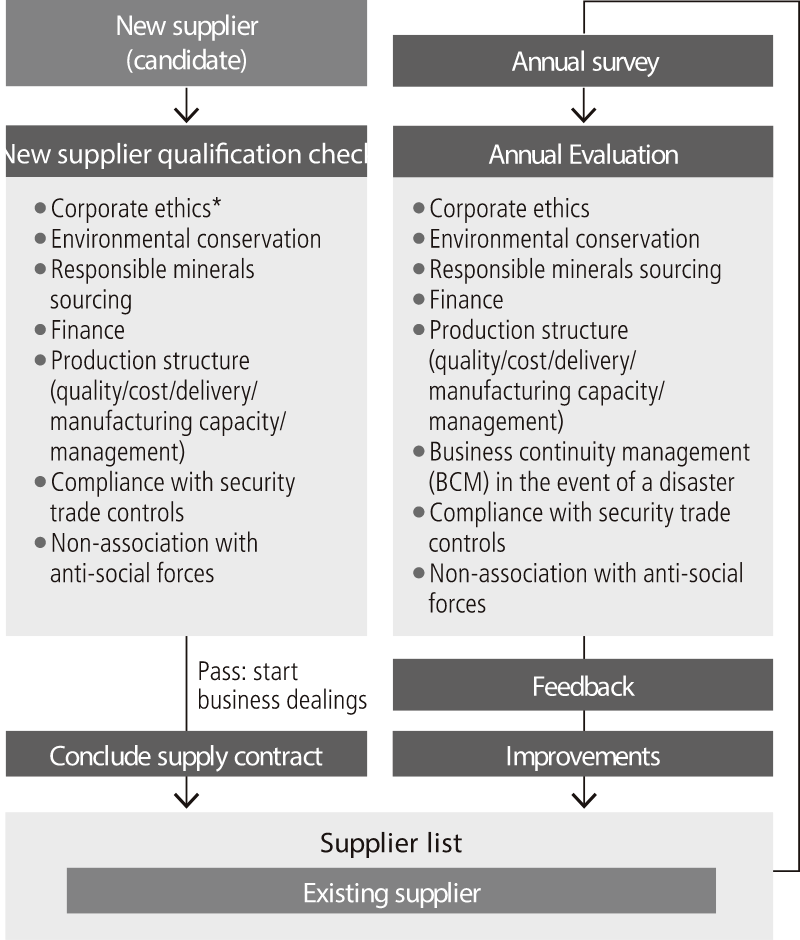
- * Corporate ethics covers areas including legal compliance, product safety, management of confidential information, human rights, labor, health and safety, and intellectual property right protection.
For parts and materials suppliers of its main business products ("major suppliers"), Canon uses an RBA-approved SAQ to identify their labor, health and safety, environmental, and ethical risks. Our 2024 survey of 378 companies elicited responses from 372 companies (representing 98.4%). Suppliers that did not reply to the survey were followed up individually. No businesses were identified as high risk among these suppliers, but we provided feedback on the results to our major suppliers and requested that they identify weaknesses and improve on them.
We also conduct online meetings and arrange site visits to help verify the SAQ responses of a select number of major suppliers around the world. During on-site inspections, we check that suppliers have instituted proper policies and internal regulations relating to labor, health and safety, the environment, ethics and supplier management, and that the systems for formulating and managing annual plans for environmental performance targets are functioning effectively. Recognizing the need to reinforce systems for compliance with the RBA Code of Conduct, we also confirm that suppliers and Canon should be committed to working together to achieve continuous improvements.
Example of Items Checked in On-site Inspection
- Availability of hotline for reporting harassment and related compliance processes
- Condition of firefighting and fire protection equipment/systems and emergency exits
- Regulations for using personal protective equipment and managing chemicals; implementation of OHS education activities
- Records of target-setting and plans for cutting usage of energy and hazardous substances, plus related reviews
- Whether code of conduct and policies are widely known
We also request major suppliers to sign an agreement concerning the RBA Code of Conduct. In 2024, agreements were signed with 371 of 378 major suppliers, equating to a consent rate of 98.1%.
Since 2022, at our core business production sites, we have also been carrying out risk assessments relating to labor, health and safety, the environment, and ethics, for the major onsite service providers related to security, cleaning, and cafeteria, labor agencies, and facility or dormitory management companies. The assessments conducted in 2024 identified risks mainly in the following areas, and we worked for improvement in collaboration with suppliers.

Charge for Expenses Incurred for Employment
In line with a company rule, employees were being charged for essential work items such as uniforms and tools. After requesting that charges be refunded and the company regulations revised, we checked that the rule had been changed.
Prohibition on Punitive Fines
Disciplinary regulations included fines and pay cuts. Since these are not permitted under RBA standards, we requested that the company revise its regulations. Later, we checked that the rules had been revised.
Appropriate Pay Slips
Since short-term workers were not receiving details of their paid hours or rates, we advised the company to provide them more detailed wage statement.
Physically Demanding Work
We requested a review of the work standards to ensure that tasks requiring the transportation of heavy objects (over 50 pounds) are carried out by two or more people. Additionally, we confirmed that pregnant women are not assigned tasks involving heavy objects.
Management of Personal Information
With a supplier where the access to personal information about employees was not restricted properly, we requested that a framework of appropriate access controls be created. Later, we checked that a system involving password-setting had been established.
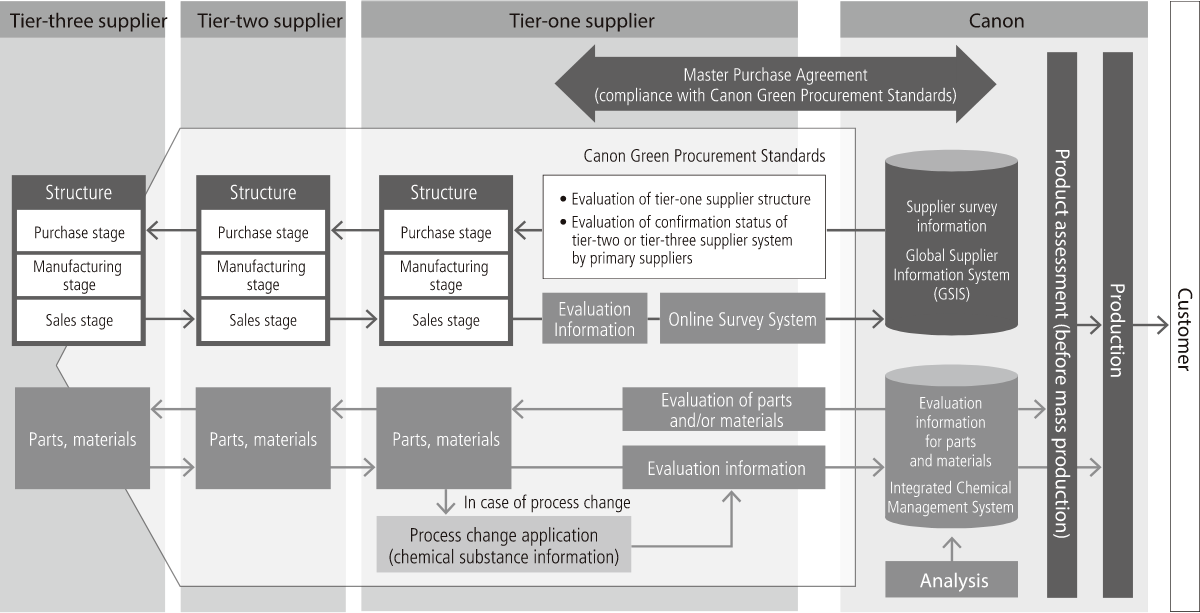
Green Procurement and Guidance to Suppliers
In the environmental area, Canon has established Canon Green Procurement Standards, which outline its environment-related requests to suppliers. Suppliers must comply with these standards to do business with Canon. Specifically, we view a supplier's environmental management as consisting of two interrelated elements: management of business activities, and management of parts and materials. We require that the supplier must operate effective environmental management in each of the four frameworks labeled A-D in the diagram below. If a supplier is found to have a negative impact on the environment, we immediately demand corrective action be taken and check the status of improvements made.
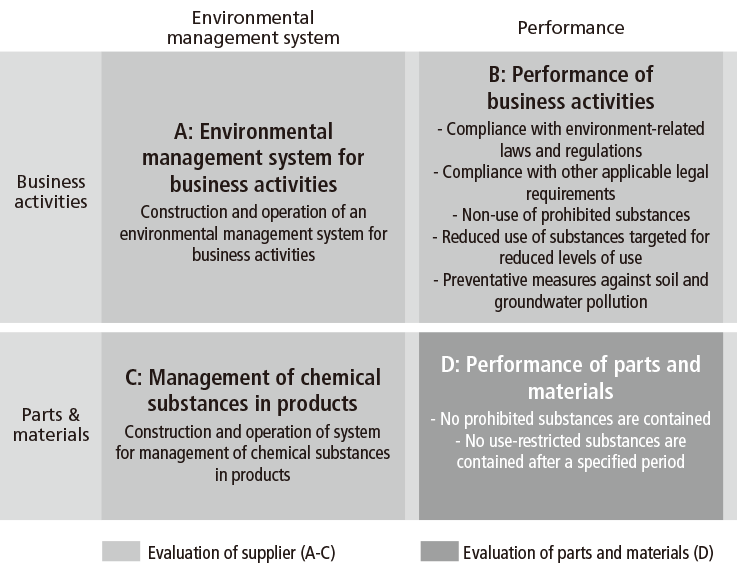
To promote environmental conservation activities, we require Canon suppliers throughout the supply chain to work for environmental impact reduction in their business activities by putting in place and operating an environmental management system. Specifically, regarding the chemical substance content of products, alongside the requirements of our Green Procurement Standards, we have designed and deployed a system for managing information on the content of such substances in parts and materials to prevent the possibility of product contamination with prohibited substances.
It was already Canon's practice to check the organization and environmental performance of a supplier's business activities and any corrective measures taken. Now, we have further strengthened our risk management to help prevent pollution in our supply chain. For example, in order to ensure compliance with stricter regulations, we are taking measures to boost information gathering and analysis activities regarding laws and regulations on wastewater and emissions in emerging countries. We also conduct risk management in plating processes, where there is a relatively high risk of environmental pollution associated with wastewater treatment as a certain volume of heavy metals is used. Expanding the scope of risk management in this way helps ensure pollution prevention.
Reduction of Supply Chain Environmental Risk in Partnership with China's Institute of Public & Environmental Affairs (IPE)
Based on supply chain information published by the Institute of Public & Environmental Affairs (IPE), a Chinese environmental NGO, we help secondary and tertiary suppliers and other Chinese businesses located in the upstream of the supply chain to reduce environmental risk by making recommendations and carrying out improvements. By sharing information regularly and communicating with the IPE on best practice, we contribute to reducing environmental risk throughout the supply chain.
Cooperation with Suppliers
Canon is enhancing its cooperative relationships with suppliers through implementation of the EQCD concept.
Specifically, as part of our environmental initiatives, we are working in partnership with suppliers to reduce CO2 emissions using varied measures such as emissions visualization and the adoption of parts and materials with lower CO2 emissions; to promote materials recycling; and to promote regulatory compliance relating to chemical substances.
In addition, as part of our initiatives to improve quality, besides clarifying evaluation standards, we are looking at cooperative approaches that utilize supplier feedback to help raise quality.
Through these types of communication, we aim to share information with suppliers, strengthen collaboration, and grow together.
Hotline for Risks in the Supply Chain
Canon has set up a hotline to allow anyone inside or outside the company to anonymously report any concerns about the supply chain. This enables whistleblowers to share any specific concerns or information relating to human rights or other responsible business practices, such as instances of child labor or forced labor. This process is detailed in the Canon Supplier Code of Conduct and publicized.
Addressing the Issue of Responsible Minerals Sourcing
Products manufactured and sold by the Canon Group and numerous other corporations contain materials that originate from a variety of minerals. These materials are sourced through diverse supply chains from their places of origin throughout the world. Mineral mining sites, smelters or other processing sites for some of those materials have been shown to have links to armed groups, serious human rights violations or environmental destruction. Corporations are therefore being called upon to exercise their social responsibility by identifying conflict/high-risk regions and avoiding the use of materials supplied from business operators disrespecting human rights or environmental conservation in those regions.
To reassure customers using Canon products, we are working with suppliers and industry bodies on responsible mineral sourcing initiatives.
Canon Group Basic Policy on Responsible Minerals Sourcing
Due Diligence
Canon investigates the countries of origin of minerals and exercises due diligence, following the 5-step framework recommended by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) in its Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Supply Chains of Minerals from Conflict-Affected and High-Risk Areas (OECD Guidance).
Based on a common Group-wide policy and survey reporting system, Canon identifies products that could contain certain metals or minerals and then conducts investigations of the parts and materials in question, tracing up the supply chain to determine places of origin. Canon exercises due diligence to identify human rights and environmental risks in conflict-affected and high-risk areas around the world.
Risk Identification and Evaluation
Tin, tantalum, tungsten and gold (3TG) produced in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and neighboring countries are said to have been used in some cases to provide funding for armed groups allegedly responsible for serious human rights violations, environmental destruction, illegal mining, and other issues. These are generally referred to as "conflict minerals." Canon conducts research and risk assessments for 3TG sourced from high-risk regions around the world due to conflict or other factors, including the DRC and neighboring countries.
Moreover, there has been heightened worldwide attention in recent years to the procurement risk associated with non-3TG mineral substances. Specifically, cobalt — used in lithium-ion batteries and other applications — is the focus of concern over potential human rights violations, including child labor, at mining locations. Canon began assessing cobalt procurement risks in 2021.
In identifying and evaluating the above risks, Canon uses the Conflict Minerals Reporting Template (CMRT) and the Extended Minerals Reporting Template (EMRT) published by the Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI*), as well as internally developed formats based on survey indicators where necessary. We use the results of these surveys to inform risk-mitigation efforts in this area.
- * An international program that plays a leading role in the response to conflict minerals.
Initiatives to Reduce Risk
Supplier cooperation is essential in identifying places of origin for minerals and related smelters. Besides assisting eligible suppliers by compiling a guidance manual for our surveys, we also encourage suppliers to ascertain and use only those smelters confirmed as conformant by the RMI. Where significant risk is found, we seek to mitigate it by requesting that suppliers switch to a supply chain with lower mineral procurement risk.
Canon established a page entitled "Procedure for the Submission of Concerns Regarding Mineral Risk" on its official website to recognize such risks in the early stage. Parties with specific concerns and/or information regarding circumstances of extraction, trade, handling and export of minerals in conflict-affected and high-risk areas as they pertain to Canon product supply chains (such as facts indicating that those minerals are the source of funds for armed groups in conflict-affected areas and human rights violations) can contact Canon through this page.
Procedure for the Submission of Concerns Regarding Mineral Risk
Cooperation with Industry Groups
Since April 2015, Canon has supported the activities of the RMI, an international program focused on addressing the issue of conflict minerals.
In Japan, Canon is active as a leading member of the Responsible Minerals Trade Working Group (RMTWG) of the Japan Electronics and Information Technology Industries Association (JEITA).
2024 Surveys and Disclosure
In 2024, Canon requested CMRT/EMRT-based surveys relating to 3TG and cobalt sourcing from eligible suppliers. The response rates were approximately 90% for 3TG and 83% for cobalt (tentative response rate as of March 14, 2025).
Based on the survey responses, there is no evidence pointing towards significant human rights or environmental risks in Canon's supply chain. However, the complex nature of the supply chain makes it difficult to identify specific smelters or in many cases to obtain clear responses. Given these and a range of other survey challenges, Canon is working for further risk identification and improvement.
In line with OECD Guidance, the assessment framework of Canon Group surveys, the results, risk analyses and information relating to specific smelters are published annually in the Conflict Minerals Report on Canon's website.
The Responsible Minerals Sourcing Report (3TG) is audited by independent private-sector experts to provide some assurance that the Group's initiatives on conflict minerals investigation conform to international standards in the form of the OECD Guidance.
A total of 22 Canon Group production sites underwent VAP audits by the RBA in 2024. Canon was recognized as being compliant with standards for 'D. Ethics 7. Responsible Mineral Sourcing' of the RBA Code of Conduct.
| Conflict Minerals Report (June 10, 2024) (2.6MB) |
Compliance with Modern Slavery Act
Modern slavery laws mandate enterprises of a certain scale that operate in a target jurisdiction to publish annual statements detailing the risk of forced labor, human trafficking and child labor in their own operations and supply chain. Such laws have been enacted in the UK (2015), Australia (2018) and Canada (2024). Canon group companies falling within the scope of the laws publish annual statements, based on the information on human rights risk assessments conducted by Canon Group production sites and suppliers.
Annual statements are also published by Canon Medical and Axis in compliance with this legislation.
